Understanding Shoulder Instability
The shoulder is the most flexible joint in the body. It allows you to throw a ball, scratch your back, and reach in almost any direction. But if your shoulder joint is injured, it may become unstable. This is called shoulder instability.
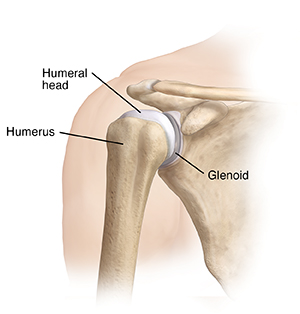
A healthy, stable shoulder
The head of the arm bone (humerus) rests in a socket (glenoid), much like a golf ball fits on a tee. Parts of the joint called stabilizers hold the humeral head and glenoid together. These include a sheet of ligaments and other tough fibers called the capsule. This encloses the humeral head and glenoid.
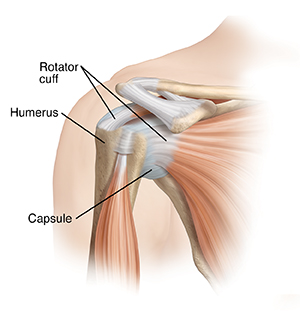
A loose, unstable shoulder
The leading cause of instability is an injury that forces the humeral head out of its socket. If the humerus pushes completely out of the socket, it’s called a dislocation. If it only pushes partially out, it’s called a subluxation. In both cases, the injury stretches or tears fibers in the capsule. It can also damage other parts of the joint. This makes the humeral head more likely to slip out of the glenoid again.
Making your shoulder stable again
Your healthcare provider will evaluate your shoulder. This will likely include imaging tests, such as X-rays and often an MRI. You’ll then discuss treatment choices. These can include physical therapy, surgery, or both. After the shoulder is stabilized, proper exercise can help keep it that way.